Trending CVEs for the Week of February 25th, 2019
- Feb 28, 2019
- Shawn Evans
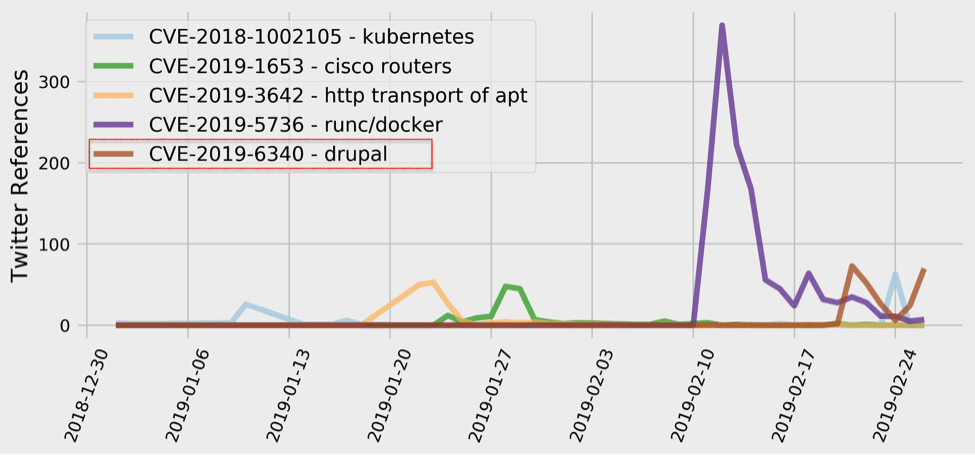
This week’s most tweeted-about vulnerability is a, yet another, highly critical remote execution flaw in Drupal – CVE-2019-6340. The Docker container escape vulnerability that has been dominating the past couple of weeks is still the most talked about vulnerability of 2019, but the mentions appear to be diminishing rapidly.

Drupal is a very popular open source web-based content management system (CMS). It is used to create rich, dynamic web applications. With almost 5% market share, it is the third most used CMS, right behind WordPress and Joomla. According to Drupal, it is the platform that governments of the United States, London, and France use to communicate with its citizens, the framework that media companies like BBC and NBC rely on to inform and entertain, and a part of how organizations and universities like Amnesty International and University of Oxford work on making the world a better place.
In the security world, Drupal is already infamous for vulnerabilities such as Drupalgeddon – October of 2014 series of SQL injection flaws, and Drupalgeddon 2.0. – March/April of 2018 remote command execution vulnerabilities that impacted over a million sites running Drupal and resulted in large scale automated attacks against those sites.
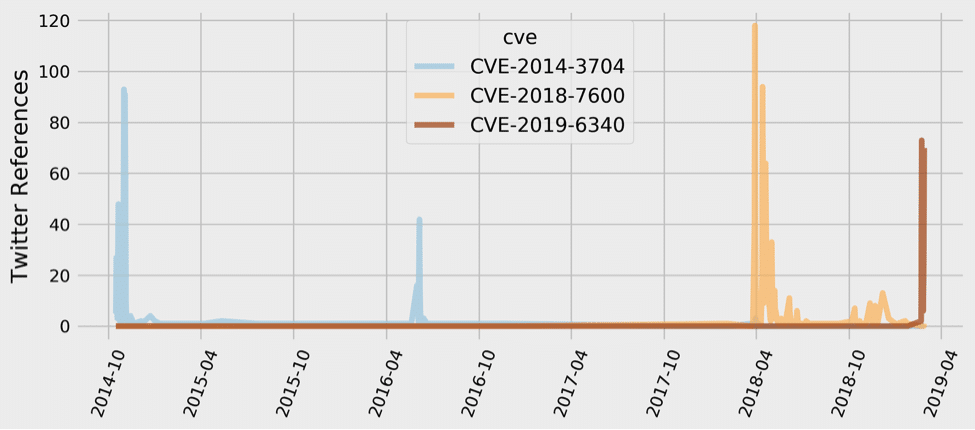
The newest Drupal vulnerability, CVE-2019-6340, is due to improper input validation in Drupal 8.5.x before 8.5.11 and Drupal 8.6.x before 8.6.10. This can lead to arbitrary PHP code execution and allow remote attackers to take over a Drupal site. The vulnerability can be exploited by simply sending one request to the server, and has been labeled as highly critical by Drupal (CVSS V2 is 6.8 – medium, CVSS V3 is 8.1 – high; however, the NVD description needs updating to reflect an additional exploitation path, more details below).
Drupal 8.5.x before 8.5.11 and Drupal 8.6.x before 8.6.10 are affected.
A site is affected if one of the following conditions is met:
The Drupal security team has confirmed that there are known mass exploits being reported in the wild and that there exists an additional exploit path that was not originally reported – any enabled REST resource endpoint, even if it only accepts GET requests, is vulnerable. Originally, and as currently reflected in the NVD description, it was indicated that the vulnerability may be mitigated by blocking POST, PATCH and PUT requests to web services resource.
In fact, multiple reports confirm that it took hackers only three days to start launching attacks against Drupal websites. The attackers, as detected by web firewall company Imperva, tried to inject a Javascript cryptocurrency miner called CoinIMP on vulnerable sites.
According to Imperva, the attacks began three days after Drupal patched the vulnerability, and two days after proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code became available online. ZDNet report notes that while these events resemble the events surrounding Drupalgeddon 2, which took months to patch and was exploited as late as last fall, this new bug has a smaller attack surface
with an estimated number of vulnerable sites being significantly lower since Drupal 7 is still the more popular version of Drupal.
A day before the NVD publication, Drupal released a security update that fixes CVE-2019-6340.
The solution is to upgrade to the most recent version of Drupal core:
To immediately mitigate the vulnerability, it is also possible to disable all web services modules, or configure your web server(s) to not allow GET/PUT/PATCH/POST requests to web services resources.
Drupal Security Advisory for Increased Risk
Imperva Report on Attempted Attacks
ZDNet Report on Attempted Attacks
Share your thoughts in our community!